Breaking News
Oklahoma legislature increases state-set rate for legal notices, enacts reforms.
Oklahoma legislators voted to override the governor’s veto of House Bill 2167 – an OPA-sponsored legal notice bill – in the final hours of the 2025 legislative session. The legislation increased the state-set legal notice rates for the first time since 2005 and included other reforms for readability and accessibility of legal notices.
HB 2167 passed the House on March 25 by an 83-6 vote. On April 28, the bill passed the Senate 36-6. On May 5, the governor vetoed the legislation, writing a confusing and surprising veto message, even though the bill reached his desk with veto-proof vote majorities in both the House and Senate.
OP-ED: Legal Notices under attack – again (HB 1080)
Whitesboro News-Record (TX) April 03, 2025, by Austin Lewter
To anyone who says, “Newspapers are dead,” I say, “Sit at my desk the Monday after the post office sends a bundle of newspapers to Fort Worth by mistake.”
I say, “Answer my phone when someone has a neighbor whose dog ate their paper.”
I say, “Do my job when someone forgot to renew their subscription on time and, all of a sudden, realized they didn’t get their paper that week.”
The latter two incidents are far more common than the former, but they all occur from time to time. When they do, I field calls from frustrated readers looking for their paper.
May 2025 Monthly Newsletter
Thank you to Richard Karpel for his dedication to protecting public notices.
Best Wishes on his retirement.
Jim Tarrant and Lisa McGraw look forward to working collaboratively with you to
- expand accessibility to public notices for the public while
- maintain the role of trusted local newspapers, as a disinterested, third-party or
- evolve to the digital descendant of a printed newspaper
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania NewsMedia Association supports bill to update Public Notice
State-agency website bills dead in three states
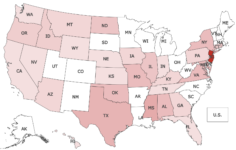 Legislation requiring state agencies to publish official notice on their websites was killed last week in committees in Indiana, Georgia and West Virginia.
Legislation requiring state agencies to publish official notice on their websites was killed last week in committees in Indiana, Georgia and West Virginia.
After passing the House last month by a comfortable margin, Indiana HB-1312 was defeated in a Senate committee by a vote of 8-2. The bill allowed every public notice in the state to eventually be posted on a state-agency website. It was rejected a week after the Hoosier State Press Association (HSPA) organized a statehouse rally at which “more than 100 Indiana publishers, editors, reporters and subscribers gathered outside the Senate chambers” to oppose the bill, according to Johnston County’s Daily Journal.
Press association websites essential for survival of newspaper notice
 Legislation designed to move all official notice to a single state-agency website has been introduced this year in Georgia, Idaho, Indiana, New Jersey and West Virginia. The bills in Indiana, Georgia and West Virginia are already dead (see story above) and those in Idaho and New Jersey appear unlikely to pass.
Legislation designed to move all official notice to a single state-agency website has been introduced this year in Georgia, Idaho, Indiana, New Jersey and West Virginia. The bills in Indiana, Georgia and West Virginia are already dead (see story above) and those in Idaho and New Jersey appear unlikely to pass.
But these types of bills probably pose the most serious long-term threat facing newspaper notice. They are fully subsidized by taxpayers and force newspapers to compete with the most well-resourced organization in every state: The executive branch of the state government.
PNRC and ACCN announce management change
 The boards of directors of the Public Notice Resource Center (PNRC) and American Court and Commercial Newspapers (ACCN) announced last month that they have selected the Michigan Press Association (MPA) to manage the joint affairs of the two groups when the contract with their current management company ends on April 2.
The boards of directors of the Public Notice Resource Center (PNRC) and American Court and Commercial Newspapers (ACCN) announced last month that they have selected the Michigan Press Association (MPA) to manage the joint affairs of the two groups when the contract with their current management company ends on April 2.
PNRC is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization that promotes government and corporate transparency through research and education focused on how to provide effective official notice to the public. It is the only national organization that monitors and analyzes public notice legislation in all 50 states. ACCN is a trade association that represents local newspapers that report on and provide services to the legal and business communities in which they operate.
Three states edge closer to government website notice
 Legislation that would move all or most public notice in three states to government websites passed significant milestones last month. Bills in Indiana and Kentucky were approved by the Houses of Representatives in those states by comfortable margins, while another in Idaho’s lower chamber barely squeaked by.
Legislation that would move all or most public notice in three states to government websites passed significant milestones last month. Bills in Indiana and Kentucky were approved by the Houses of Representatives in those states by comfortable margins, while another in Idaho’s lower chamber barely squeaked by.
The most significant threat to newspaper notice appears to be the assault launched in Indiana, where HB-1312 would eventually allow all public and private notices in the state to be posted on a website established by the Indiana Office of Technology (IOT). It passed the House on Feb. 18 by a 57-36 vote.
Two state press groups prepare for future
 Print is still the most effective platform for public notice but declining circulation and newspaper closures have put newspaper notice in peril. In 2025, two state press associations are promoting bills designed in part to avoid the kind of crises that erupted last year in Minnesota and New Jersey when newspaper chains in those states shuttered papers that had served as their communities’ only source of official notice.
Print is still the most effective platform for public notice but declining circulation and newspaper closures have put newspaper notice in peril. In 2025, two state press associations are promoting bills designed in part to avoid the kind of crises that erupted last year in Minnesota and New Jersey when newspaper chains in those states shuttered papers that had served as their communities’ only source of official notice.
One of the most far-reaching efforts to prepare for the future is being advanced by the Oklahoma Press Association. OPA supports two bills that together:
- Expand the number of papers eligible to publish official notice
N.J. press group backs extraordinary public notice measures
 When we last reported on New Jersey, the state faced a public notice crisis triggered by the news that the Newhouse media empire’s Star-Ledger, the state’s largest and most significant newspaper, planned to shutter its print edition on Feb. 1, along with a sister publication and several affiliated newspapers. The state legislature temporarily suspended the crisis on the final day of 2024, when it enacted AB-5151, giving itself two months to amend the Garden State’s public notice laws and come up with a solution.
When we last reported on New Jersey, the state faced a public notice crisis triggered by the news that the Newhouse media empire’s Star-Ledger, the state’s largest and most significant newspaper, planned to shutter its print edition on Feb. 1, along with a sister publication and several affiliated newspapers. The state legislature temporarily suspended the crisis on the final day of 2024, when it enacted AB-5151, giving itself two months to amend the Garden State’s public notice laws and come up with a solution.
Legislative floodgates open
 Every January, we are inundated with a firehose of public notice bills gushing from legislatures ranging from Connecticut to California and most states in-between. This year has been no different. PNRC is now following 83 separate pieces of legislation which almost certainly doesn’t include many other most-likely minor bills we haven’t been able to catch up with yet.
Every January, we are inundated with a firehose of public notice bills gushing from legislatures ranging from Connecticut to California and most states in-between. This year has been no different. PNRC is now following 83 separate pieces of legislation which almost certainly doesn’t include many other most-likely minor bills we haven’t been able to catch up with yet.
Alaska newspapers form coalition; public notice looms large on agenda
 When 2024 began, Alaska may have been the only state in the U.S. where newspapers lacked any semblance of an organized effort to protect their interests. That ended early last year when a group of newspaper supporters established the Alaska News Coalition (ANC) under the auspices of the Juneau Community Foundation.
When 2024 began, Alaska may have been the only state in the U.S. where newspapers lacked any semblance of an organized effort to protect their interests. That ended early last year when a group of newspaper supporters established the Alaska News Coalition (ANC) under the auspices of the Juneau Community Foundation.
One year later the group has made tremendous progress, establishing a governing body and attracting the initial funding that will allow it to begin representing newspapers in the state in earnest. The protection of public notice is at the top of its to-do list.
