 Most newspapers now publish notices on their website in addition to print, even in states that don’t require it. As we’ve written before, it’s one of the most important things publishers can do to help their state’s press association protect newspaper notice.
Most newspapers now publish notices on their website in addition to print, even in states that don’t require it. As we’ve written before, it’s one of the most important things publishers can do to help their state’s press association protect newspaper notice.
However, too many publishers still make it difficult for users to find the notices that are posted on their website. Last week we spotted a perfect illustration of the phenomenon.
The Westerly Sun published an editorial (“In defense of legal notices”) arguing against legislation that has been introduced in Rhode Island’s General Assembly that would allow local governments to publish notices on their websites in lieu of print newspapers. A website visitor quickly added a helpful suggestion in the comments section below the article.
Several eligibility and self-storage bills advance
 It’s the time of year when many states have either ended their legislative sessions or are preparing to adjourn sine die in the next month or so. We’ve also passed the point in most states when new bills can be introduced or existing legislation that hasn’t passed out of the body in which it was introduced can be considered in the opposite chamber.
It’s the time of year when many states have either ended their legislative sessions or are preparing to adjourn sine die in the next month or so. We’ve also passed the point in most states when new bills can be introduced or existing legislation that hasn’t passed out of the body in which it was introduced can be considered in the opposite chamber.
Nevertheless, several noteworthy public notice-related bills we’ve been following did see some movement last month.
Most importantly, bills in Arizona and Iowa authorizing local governments to publish notices on government websites instead of newspapers were significantly amended before they passed their original chambers.
About those Disney notices …
 You may have heard that the Walt Disney Co. recently took steps to frustrate Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis’ attempt to strip the entertainment conglomerate of its power to appoint members of the board that provides oversight for Disney World.
You may have heard that the Walt Disney Co. recently took steps to frustrate Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis’ attempt to strip the entertainment conglomerate of its power to appoint members of the board that provides oversight for Disney World.
According to a story published last week in the New York Times, the Disney-appointed Reedy Creek Improvement District (RCID) Board of Supervisors “quietly pushed through a development agreement” preventing the governor from replacing them with his allies, thereby maintaining Disney’s governance of the world’s largest theme park. The Board proposed the agreement at a public meeting on Jan. 25 and approved it at a follow-up meeting on Feb. 8.
Trends emerge in public notice bills
 It used to be a relatively rare event when a bill remedying errors or omissions in public notice advertising was introduced. Or when legislation authorizing newspaper websites or e-editions to substitute for print was proposed. But those types of measures have proliferated in 2023, along with bills designed to fill jurisdictional holes in news deserts, which have been picking up steam for a few years now.
It used to be a relatively rare event when a bill remedying errors or omissions in public notice advertising was introduced. Or when legislation authorizing newspaper websites or e-editions to substitute for print was proposed. But those types of measures have proliferated in 2023, along with bills designed to fill jurisdictional holes in news deserts, which have been picking up steam for a few years now.
Newspapers battle in 2 states over right to publish notices
 Most states require newspapers to have paying subscribers to publish notices but at least a few grant that authority to free-distribution papers as well. Those requirements don’t change very often which is why it’s so unusual to have two states considering legislation this year that would allow free papers to publish notices.
Most states require newspapers to have paying subscribers to publish notices but at least a few grant that authority to free-distribution papers as well. Those requirements don’t change very often which is why it’s so unusual to have two states considering legislation this year that would allow free papers to publish notices.
The newspapers supporting the measures in both states were founded by entrepreneurs in communities where the paid-circulation newspapers have experienced multiple rounds of layoffs and cutbacks in recent years. Taking the other side of the debate are the states’ press associations, both of which oppose the bills.
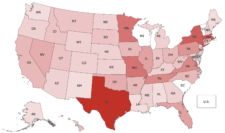
Newspaper notice targeted in multiple states
 Bills have been introduced in at least 15 states allowing or requiring official notice to be published on various platforms other than local newspapers. That’s significantly more legislative activity focused on replacing newspaper notice than last year and approaches the level of the previous election off-year of 2021.
Bills have been introduced in at least 15 states allowing or requiring official notice to be published on various platforms other than local newspapers. That’s significantly more legislative activity focused on replacing newspaper notice than last year and approaches the level of the previous election off-year of 2021.
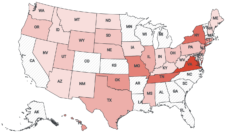
What happens after the bill passes?
 For over 20 years, newspapers and their state press associations turned back every bill that authorized government units to issue public notice via their own websites instead of local newspapers. That winning streak ended last year when the Florida legislature gave state agencies and local governments the option to post notices on county websites.
For over 20 years, newspapers and their state press associations turned back every bill that authorized government units to issue public notice via their own websites instead of local newspapers. That winning streak ended last year when the Florida legislature gave state agencies and local governments the option to post notices on county websites.
The new law, which took effect on Jan. 1, has one upside. It set in motion a vast experiment that will tell us what local governments do when given this choice. Five weeks into the new year an answer is beginning to emerge: It depends primarily on the motivations of local elected officials and the actions local newspapers take in response to the challenge.
Colorado paper prevails in public notice case
 The Wet Mountain Tribune in December settled its slam-dunk federal lawsuit against the Custer County Board of Commissioner (BOCC) and will once again run the county’s public notices. The lawsuit claimed the BOCC violated the Tribune’s First Amendment rights by retaliating against it by awarding the county’s public notice contract to another local newspaper that is openly partisan.
The Wet Mountain Tribune in December settled its slam-dunk federal lawsuit against the Custer County Board of Commissioner (BOCC) and will once again run the county’s public notices. The lawsuit claimed the BOCC violated the Tribune’s First Amendment rights by retaliating against it by awarding the county’s public notice contract to another local newspaper that is openly partisan.
In addition to making the Tribune the county’s official newspaper again for the next four years, Custer County also agreed to pay the Tribune $50,000. That’s about three times as much as the county spends annually on its notices, according to Tribune owner Jordan Hedberg’s (photo above) estimate.
Public Notice Year in Review
 When Gov. Ron DeSantis signed House Bill 7049 in May, Florida became the first state to enact a law allowing local governments to publish notices on their own websites rather than in newspapers.
When Gov. Ron DeSantis signed House Bill 7049 in May, Florida became the first state to enact a law allowing local governments to publish notices on their own websites rather than in newspapers.
But the big takeaway in Florida turns out to be that the passage of the bill was only the beginning of the story, not the end. Local governments in the Sunshine State don’t appear to be in a rush to abandon newspaper notice when HB-7049 takes effect on Jan. 1. In fact, the only county that has formally considered the issue decided to stick with newspapers. Public officials’ response to the new law is proving the enduring efficacy of providing official notice via local newspapers.
Expanding public notice eligibility requirements
 The newspaper industry that existed when public notice laws were originally enacted is a thing of the past. There are fewer newspapers and they have less circulation. The papers are physically smaller and sometimes they’re designed, edited and/or printed at great geographical distances from the local markets in which they circulate. They’re also published electronically with a reach and immediacy that were unprecedented in the pre-internet era.
The newspaper industry that existed when public notice laws were originally enacted is a thing of the past. There are fewer newspapers and they have less circulation. The papers are physically smaller and sometimes they’re designed, edited and/or printed at great geographical distances from the local markets in which they circulate. They’re also published electronically with a reach and immediacy that were unprecedented in the pre-internet era.
These changes have made it increasingly difficult for newspapers and government agencies to discharge their responsibilities under public notice laws enacted many decades ago. As a result, state press associations otherwise reluctant to meddle with public notice statutes now may find it necessary to advocate for changes to ensure the laws that determine which papers qualify to publish notices remain relevant.
